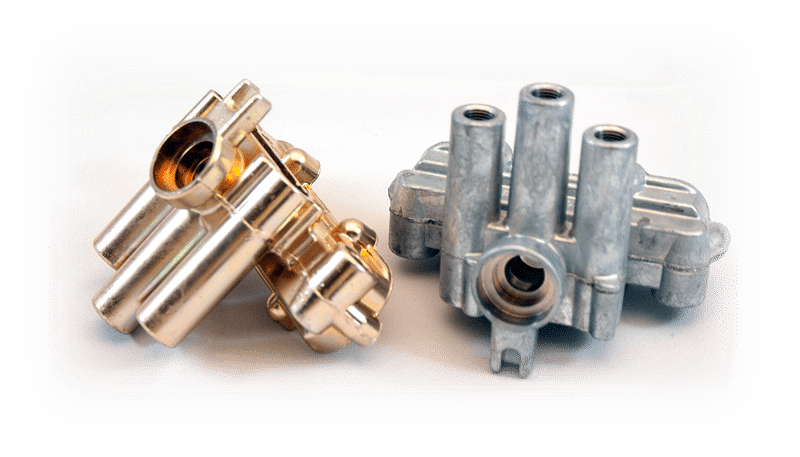
At our company, we understand the importance of finding effective ways to improve the wear resistance of materials used in various applications. One of the most effective methods we have found for achieving this is through the process of zinc plating. In this article, we will provide an in-depth look at how this process can improve wear resistance, as well as the various benefits and applications of this process.
Understanding Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is a process where a thin layer of zinc is applied to the surface of a metal substrate. This is achieved through a process known as electroplating, where an electric current is used to deposit the zinc onto the surface of the metal. This process is an effective way to provide corrosion resistance to metals, as well as to improve their wear resistance.

Early Development of Zinc Plating
The process of electroplating was first discovered in 1805 by Italian chemist Luigi Brugnatelli. He discovered that he could coat a piece of silver with gold by immersing it in a solution containing gold particles and passing an electrical current through the solution. This discovery led to the development of electroplating, which involves coating an object with a thin layer of metal through electro-deposition.
In the 1830s-40s, the process of electroplating was further developed by English chemist John Wright. He discovered that he could coat iron objects with a layer of zinc by immersing them in a solution containing zinc particles and passing an electrical current through the solution. This process became known as zinc plating.
The Rise of Zinc Plating in Industry
During the late 1800s and early 1900s, zinc plating became a widely used method of protecting metal objects from corrosion. It was commonly used in the automotive industry to protect car bodies and parts from rust and corrosion. It was also used in the construction industry to protect steel beams and other metal objects from the elements.
The use of this process in industry continued to grow throughout the 20th century. It became a popular method of protecting metal objects in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, aviation, and marine.
Advancements in Zinc Plating Technology
Over the years, advancements in technology have led to improvements in the zinc plating process. One major advancement was the development of alkaline zinc plating in the 1960s. This process involves the use of an alkaline solution, which allows for a thicker, more uniform layer of zinc to be deposited onto the surface of the metal object.
Another advancement in zinc plating technology was the development of trivalent chromate passivation in the 1990s. This process involves the use of a trivalent chromate solution, which is less toxic than the traditional hexavalent chromate solution. It also provides better corrosion resistance and a more uniform colour.

Zinc Plating Process
This process involves several steps, including:
Surface Cleaning
Thorough cleaning of the substrate is essential before zinc plating to remove any rust, oil, and dirt. The use of an alkaline detergent is recommended to ensure the longevity of the zinc coating. Failure to adequately clean the substrate can result in defects such as blistering or peeling. The cleaning process involves immersing the metal in a bath for 5-10 minutes at 150 to 200° F to remove any dirt. This is followed by an acid treatment to eliminate any surface rust. In some cases, an electro cleaner is used for micro-level cleaning, where an electric charge is applied to the metal at its anode or cathode end.
Proper cleaning is critical to ensure the effectiveness of zinc plating. The substrate must be free of any contaminants, including dirt, grease, or other substances, to achieve optimal adhesion of the zinc coating. Therefore, it is important to follow the appropriate cleaning procedures to achieve the desired results. By doing so, this process will be more effective and last longer, providing protection against corrosion and other types of damage.
Pre-treatment
The substrate must also undergo pre-treatment before zinc plating. Pre-treatment involves applying a thin layer of zinc phosphate or chromate conversion coating to the substrate. This pre-treatment helps to improve the adhesion of the zinc coating to the substrate.
Zinc Plating
After completing the initial cleaning and pre-treatment of the substrate, the zinc plating process can begin. The first step is to apply a direct current (DC) at the anode end for a predetermined period of time. This causes the deposition of zinc ions onto the surface of the metal at the cathode end. To ensure uniformity in the electroplating process, the cathode and anode must be positioned correctly in an aqueous solution while ensuring that the current flows proportionately over the entire surface area.
Post-treatment
After zinc plating, the substrate may undergo post-treatment to improve the corrosion resistance and adhesion of the zinc coating. Post-treatment may involve applying a sealant or topcoat to the substrate.
2 Methods of Zinc Plating
Rack Plating
Rack plating is a method of zinc plating in which the metal parts to be plated are suspended on racks and immersed in a zinc plating solution. The racks are then lifted out of the solution and the excess zinc is rinsed off. Rack plating is typically used for larger metal parts or parts with complex shapes that cannot be easily plated using other methods.
How does Rack Plating work?
The metal parts to be plated are first cleaned and pre-treated to remove any dirt, grease, or other contaminants that may interfere with the plating process. They are then attached to racks using wires or hooks, ensuring that they are not touching each other. The racks are then dipped into a zinc plating solution, which contains dissolved zinc salts and other chemicals that help to regulate the plating process. An electrical current is then applied to the solution, causing the zinc to bond to the surface of the metal parts. Once the desired thickness of zinc has been achieved, the racks are lifted out of the solution and the excess zinc is rinsed off.
Advantages of Rack Plating
One of the main advantages of rack plating is that it allows for precise control over the plating process. The use of racks and hooks ensures that each part is evenly coated with zinc, and the plating solution can be adjusted to achieve the desired thickness and appearance. Rack plating is also a good choice for larger or more complex parts that cannot be easily plated using other methods.
Barrel Plating
Barrel plating is a method of zinc plating in which the metal parts to be plated are placed in a barrel or drum along with zinc plating solution. The barrel is then rotated, causing the parts to tumble around and come into contact with the plating solution. Barrel plating is typically used for smaller metal parts or parts with simple shapes that can be easily coated using this method.
How does Barrel Plating work?
The metal parts to be plated are placed in a barrel or drum along with a zinc plating solution. The barrel is then rotated, causing the parts to tumble around and come into contact with the solution. An electrical current is applied to the solution, causing the zinc to bond to the surface of the parts. Once the desired thickness of zinc has been achieved, the parts are removed from the barrel and the excess zinc is rinsed off.
Advantages of Barrel Plating
One of the main advantages of barrel plating is that it is a fast and efficient process. Many small parts can be plated at once, and the tumbling action ensures that all parts are evenly coated. Barrel plating is also a good choice for parts with simple shapes that can be easily coated using this method.

How Zinc Plating Improves Wear Resistance
Improving the wear resistance of materials can be achieved through zinc plating, which offers various benefits. Firstly, it creates a protective layer on the metal substrate’s surface, shielding it from harsh environments and abrasive substances that can cause wear and tear.
Furthermore, this type of coating has a self-healing effect, wherein the zinc coating reacts with the atmosphere to generate a protective layer of zinc oxide when the metal surface is scratched or damaged. This layer aids in preventing further harm to the metal substrate and may enhance its wear resistance in the long run.
Benefits of Zinc Plating
The use of zinc plating in various applications offers a host of advantages. One of the most significant benefits is its ability to provide exceptional corrosion resistance to metals. When zinc, a highly reactive metal, is applied to a metal substrate’s surface, it reacts with the atmosphere, creating a protective layer of zinc oxide. This layer protects the metal from corrosion, even in severe conditions.
Another key advantage of This type of coating is its ability to provide superior wear resistance to materials. As previously mentioned, the zinc coating acts as a safeguard against abrasive materials and harsh surroundings, prolonging the material’s lifespan and reducing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Applications of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating exhibits numerous industrial applications, spanning automotive, marine, construction, agricultural, aerospace, and military domains. Automobile elements are frequently layered with zinc plating to forestall rusting and corrosion induced by the exposure to severe factors like saltwater or road debris. Marine functions also receive advantages from this type of coating to mitigate galvanic corrosion between non-identical metals when subjected to saline surroundings, such as salt marshes or the open sea.
Furthermore, diverse building materials, such as steel beams or fasteners, could receive a zinc plating coating to assist them in enduring unfavourable atmospheric conditions and ultraviolet light exposure while situated outdoors. Ultimately, aviation and military components may also reap benefits from this type of coating as it decreases weight while simultaneously delivering elevated tiers of robustness and longevity under extreme circumstances like high temperatures or atmospheric pressure deviations during flight procedures.
Conclusion
To sum up, zinc plating is a valuable surface treatment method that offers enhanced wear and corrosion resistance to substrates. With the aid of modern technology, the process has become more efficient and effective than ever before. This type of coating is extensively used in various industries, such as automotive, construction, electrical, and agriculture, due to its numerous benefits, such as improved appearance, enhanced durability, and cost-effectiveness. If you require a surface treatment that provides excellent wear and corrosion resistance, Dragon Metal Manufacturing in Brisbane, Australia is a reliable provider of zinc plating services. Contact us today to learn more and experience the benefits of our manufacturing solutions for yourself!