Metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling raw materials to create products, but coatings are necessary to protect metals from corrosion and wear over time. There are four main types of coatings used in metal fabrication: primer, organic, inorganic, and conversion coatings. Each type has advantages and disadvantages depending on factors such as the metal type and environmental exposure. Understanding the different types of coatings can help manufacturers and fabricators make informed decisions and achieve optimal results.
4 Types of Coatings for Metal Fabrication

Types of Coatings: Primer Coatings
Primer coatings are the first layer of coating applied to metal surfaces before the topcoat. Their primary goal is to improve adhesion between the metal surface and the subsequent coatings, as well as to enhance the metal’s corrosion protection. Some of the most common primer coatings used in metal fabrication include:
- Epoxy Primers – Epoxy primers are a two-part coating that provides excellent adhesion, durability, and chemical resistance. They are suitable for bare metal or existing coatings and are often used in automotive, marine, and industrial applications.
- Polyurethane Primers – Polyurethane primers are versatile coatings that offer good adhesion, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. They are commonly used in metal fabrication for their high-performance characteristics and compatibility with different types of topcoats.
- Zinc-Rich Primers – Zinc-rich primers contain a high concentration of zinc dust or powder, which provides cathodic protection to the metal surface, preventing corrosion from spreading. They are commonly used in steel fabrication, offshore structures, and other harsh environments.
Advantages of Using Primer Coatings
• Improves adhesion between metal surface and subsequent coatings, reducing the risk of peeling or flaking.
• Enhances corrosion protection by providing an additional barrier against moisture and other corrosive elements.
• Provides a smooth and uniform surface, improving the appearance and quality of the final product
• Extends the metal’s lifespan by protecting it from wear and tear.
Disadvantages of Using Primer Coatings
• Primer coatings increase the cost and time of the application process by adding an extra layer to the coating system.
• Improper surface preparation or application of the primer coating can result in adhesion and quality issues in the final product. • Careful selection and planning are necessary for some types of primer coatings, which may not be compatible with certain topcoats or application methods.
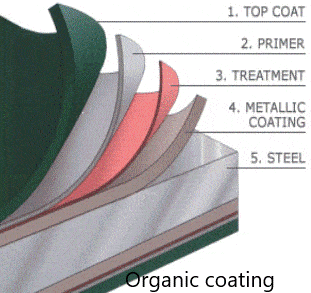
Types of Coatings: Organic Coatings
Organic coatings are protective barriers made of organic compounds, such as pigments, solvents, and resins. They safeguard metal surfaces against environmental factors, such as moisture and chemicals, that could cause corrosion or deterioration. Organic coatings come in different types, such as:
- Paints – The most common organic coatings used in metal fabrication, made of a binder, pigments, and solvents. They come in various types, such as acrylics, alkyds, epoxies, and polyurethanes, offering excellent protection against corrosion and wear.
- Varnishes – Transparent or semi-transparent coatings used to enhance the appearance of the metal while protecting it from environmental factors. They are commonly used in decorative applications, such as metal furniture, sculptures, and architectural elements.
- Powder Coatings – Organic coatings applied electrostatically and cured by heat. Available in a range of colours and finishes, they are known for their durability, chemical resistance, and environmental friendliness.
Advantages of Using Organic Coatings
• Provide an effective barrier against moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors that could cause corrosion or wear.
• Improve the appearance of the metal by offering a range of colours and finishes to choose from.
• Enhance the durability and lifespan of the metal, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
• Suitable for different types of metal fabrication projects, can be applied using a variety of methods, including spray, brush, or roller.
Disadvantages of Using Organic Coatings
• Organic coatings can be more expensive than other types of coatings, such as inorganic coatings
• Multiple coats or touch-ups may be necessary over time to maintain effectiveness
• Some organic coatings may not be suitable for high-temperature applications or harsh environments
• Application of organic coatings may require specialized equipment and trained personnel to ensure proper surface preparation and coating application.
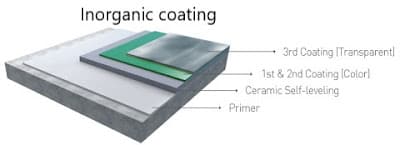
Types of Coatings: Inorganic Coatings
Coatings made from inorganic compounds, such as metals and ceramics, provide a protective barrier that prevents corrosion and wear of the metal surface. Inorganic coatings come in different types, including:
- Galvanization – Coating metal with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The zinc coating provides a sacrificial anode that corrodes instead of the metal, protecting it from rust and wear.
- Anodizing – Creating a thick layer of oxide on the surface of aluminium or its alloys. The anodized coating improves the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the metal, as well as enhancing its appearance.
- Ceramic Coatings – Inorganic coatings made from metal oxides or carbides that provide excellent resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion. They are commonly used in high-temperature and high-wear applications, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
Advantages of Using Inorganic Coatings
• Provides excellent resistance to corrosion, wear, and environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals.
• Offers long-lasting protection, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
• Provides superior heat resistance compared to organic coatings, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
• Does not release toxic substances during application or use, making them environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages of Using Inorganic Coatings
• Inorganic coatings can be more expensive than other types, such as organic coatings.
• The application process can be complex and may require specialized equipment and trained personnel.
• Inorganic coatings may not be suitable for all types of metal or applications.
• Some types of inorganic coatings may not provide a smooth and aesthetically pleasing finish compared to organic coatings.

Types of Coatings: Conversion Coatings
Conversion Coatings: Chemical treatments applied to a metal surface to improve performance and prevent corrosion are known as conversion coatings. This process converts the metal surface into a coating with better adhesion, conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
The main goal of conversion coatings is to create a surface that is receptive to a subsequent coating, such as paint or powder coating, by providing better adhesion and improved corrosion resistance. Additionally, conversion coatings can protect against moisture and other contaminants that could cause corrosion or surface defects.
Several types of conversion coatings are used in the industry, including:
- Phosphate Conversion Coatings: The reaction of a metal surface with a phosphate solution forms these coatings. The automotive and aerospace industries use phosphate coatings to improve paint adhesion and provide corrosion resistance.
- Chromate Conversion Coatings: The reaction of a metal surface with a chromate solution forms chromate coatings. These coatings are popular in the aerospace and defence industries because of their corrosion resistance and ability to improve paint adhesion.
- Anodizing: Anodizing converts a metal surface into an oxide layer using an electrolytic solution. This process is commonly used for aluminium and provides a hard, durable surface with excellent corrosion resistance.
- Passivation: Stainless steel’s corrosion resistance is improved using passivation. An acid solution is used to remove free iron and other contaminants from the surface, leaving a passive oxide layer that is resistant to corrosion.
Advantages of conversion coating
- Improved corrosion resistance
- Improved adhesion of subsequent coatings, such as paint or powder coating
- Improved surface conductivity
- Protection against environmental contaminants, such as moisture and salt
Disadvantages of conversion coating
In addition to adding an extra step to the manufacturing process:
- Some conversion coatings contain toxic materials, such as hexavalent chromium, which can pose health and safety risks to workers if not handled properly.
- Some conversion coatings, such as chromate coatings, are subject to environmental regulations due to their potential environmental impact.
Overall, the use of conversion coatings can provide significant benefits for the performance and durability of metal surfaces. However, it is important to consider the potential disadvantages and select the appropriate conversion coating for the specific application.
Metal Coating Application Methods
There are various coatings for metal fabrication that can protect and enhance the performance of the finished product. The application method used can vary depending on the specific material and desired outcome. Common application methods include spraying, brushing, and dipping for liquid coatings, electrostatic spraying for powder coatings, and a specialized approach involving chemicals and electrical currents for plating and anodizing. Immersion or spraying are the usual methods for applying conversion coatings like phosphate or chromate coatings. The choice of application method depends on factors such as the coating type, substrate material, and desired thickness and coverage.

Offshore metal manufacturing has been popular now for decades, especially in countries like China, India, Vietnam and Thailand to name a few. Despite the controversies, and the reverse trend during the Covid-19 pandemic, offshore manufacturing has proven to have numerous benefits for companies that are looking to increase production capacity, reduce costs, and improve quality. In this blog post, we will discuss 10 advantages of offshore metal manufacturing and how it can benefit the Australian manufacturing industry….
Read More about 10 Advantages of Offshore Metal manufacturing in Australia
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate coating is crucial for protecting metal fabrication products from environmental factors like corrosion and wear. Different coatings such as liquid, powder, plating, anodizing, and conversion coatings offer unique properties that can enhance the performance and appearance of the metal substrate. Each type of coating has its own advantages and disadvantages, and selection depends on factors such as the intended use, exposure environment, and desired properties of the coating. In conclusion, the right coating and application method can significantly improve the durability, appearance, and longevity of a metal product.