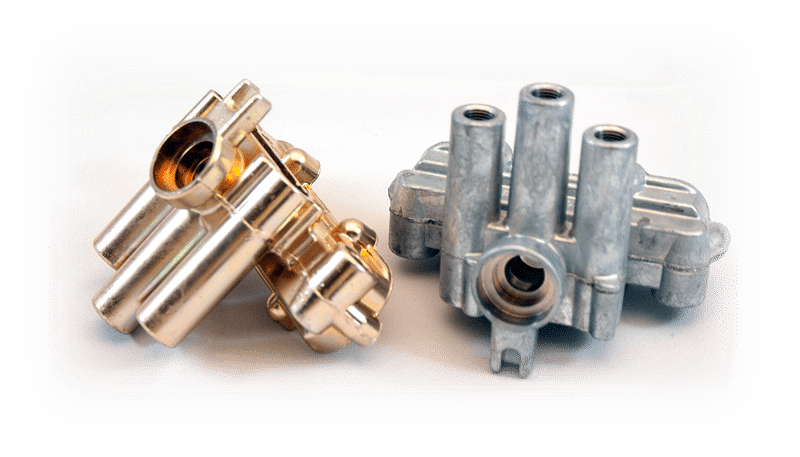
In the manufacturing industry, tooling design is a critical aspect that directly impacts the quality and cost of the final product. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of tooling design and provide practical tips to help you optimize your design process.
Understanding Tooling Design
Tooling design involves the creation of tools and fixtures that are used to manufacture products. The process is a complex one that requires a deep understanding of the manufacturing process, material properties, and design principles. A well-designed tool can significantly improve product quality, reduce manufacturing time, and lower production costs.
Key Factors to Consider in Tooling Design
To create effective tooling, several factors must be considered. These include:
Material Selection: The material used in the tooling process is critical to its performance. Factors such as strength, durability, and wear resistance must be considered when selecting materials.
Design for Manufacturability: Design should consider the ease of manufacture, assembly, and maintenance. A well-designed tool should be easy to produce, assemble and maintain.
Cost: Design can significantly impact the overall production cost. A good design should balance cost and quality, ensuring the most economical solution for the production process.

Related Article:
Tooling Design Process
The tooling design process involves several steps, including:
Requirement Analysis: The first step for this is to understand the manufacturing requirements, including the product specifications, production volume, and budget. This makes it possible to have tooling that is suitable for the parts to be moulded or cast.
Conceptualization: In this phase, designers create CAD models of the tooling and explore ways to optimize the tooling based on the final product.
Design Development: In this stage, the design is refined to develop a detailed design. This includes the creation of the final 3D models, and the preparation of engineering drawings.
Tooling production: Now that the design has been completed, the tooling can be made. The tooling time required can vary depending on multiple factors, like the material used, the complexity of the tooling and the process used.
Tool trial: Once the tooling is complete, a first trial is carried out to test the design and ensure that the end product can be made correctly.
Production: After the samples have been tested and validated, the production process begins. The tooling is set up on the machine again, and the production volume is moulded or cast, depending on the exact process used.
Software Tools
Several software tools are available to help designers create effective tooling designs. These include:

Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software: CAD software enables designers to create 3D models of tooling designs, perform simulations, and create detailed engineering drawings.

Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software: FEA software enables designers to simulate the behavior of designs under different loads and conditions, helping to optimize the design.

Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software: CAM software generates toolpaths for CNC machines, enabling the tooling design to be manufactured with precision.
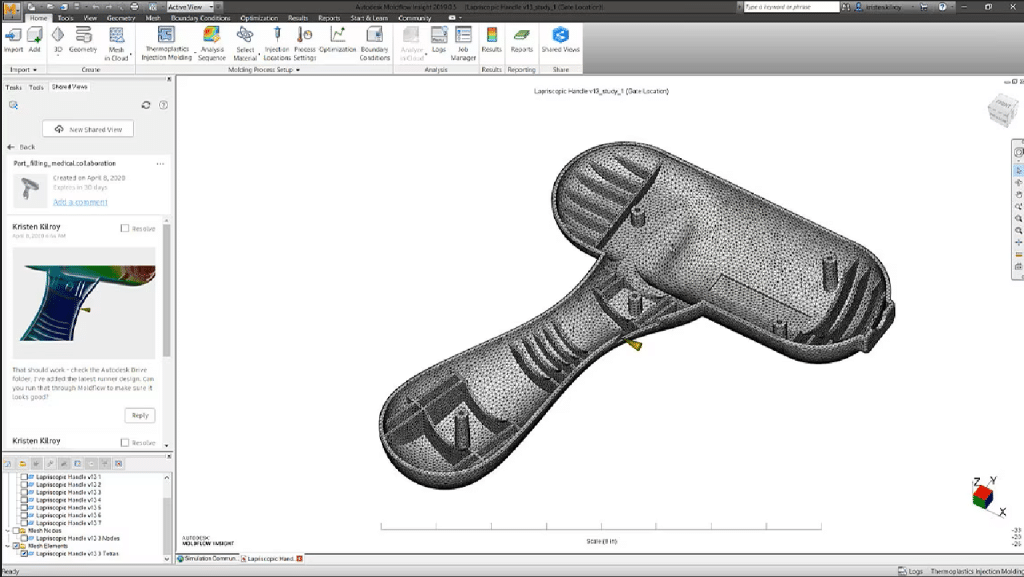
Simulation software: Software that simulates the moulding process to identify any possible difficulties in making the product. For example Moldflow.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Effective tooling design is critical to the success of the manufacturing process. By considering the key factors and following a structured design process, manufacturers can create tools that are reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality. With the right tools and software, designers can optimize their tooling designs to optimize the quality and manufacturability of their products.