Plastic extrusion is a manufacturing process that involves melting and shaping plastic materials into continuous profiles. Plastic extrusion can produce a wide range of products, such as pipes, tubes, hoses, sheets, films, rods, profiles, and more. Plastic extrusion is widely used in various industries, such as construction, automotive, packaging, medical, and consumer goods.
But not all plastic materials are suitable for extrusion. Different types of plastic have different properties, such as melting point, viscosity, strength, flexibility, durability, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and UV rays. Therefore, choosing the right plastic material for extrusion is crucial for the quality and performance of the final product. In this blog post, we will introduce some key types of plastic materials for extrusion and their characteristics. We will also discuss some factors to consider when selecting a plastic material for extrusion.

Types of Plastic Extrusion Materials
Plastic materials can be classified in different ways based on their chemical structure or commercial application. Here we will use two common classifications: commercial classification and molecular classification.
Commercial Classification
Commercially, plastic extrusion materials are grouped by their cost, market share, and material properties into three categories: commodity, engineering grade, and high performance.
Commodity Plastics are the most common and cheapest plastic extrusion materials. They account for 90% of all thermoplastic use. They are easy to process and suitable for most applications. Examples of commodity plastics include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Engineering Grade Plastics are designed with unique combinations of properties for improved performance in specific applications. They have higher mechanical strength, thermal stability, chemical resistance, or other special features than commodity plastics. Examples of engineering grade plastics include thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), polycarbonate (PC), polyamide (PA or Nylon), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS).
High Performance Plastics are engineered to have exceptional mechanical and/or thermal properties in order to meet high performance requirements in harsh environments. They are some of the most expensive plastics, so they are typically reserved for low volume, specialty applications. Examples of high performance plastics include polyether ether ketone (PEEK), polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), and polyimide (PI).
Molecular Classification
Molecularly, plastic extrusion materials are categorized by their molecular structure into two types: amorphous and crystalline.
Amorphous polymers have random and disordered molecular chains that move freely when the polymer is pushed or pulled. This gives the polymer excellent flexibility, elasticity, and impact resistance. Amorphous polymers tend to have low shrinkage and can accommodate tighter tolerances. Examples of amorphous polymers include polystyrene (PS), ABS, PC, and PET.
Crystalline polymers have ordered and regular molecular chains that form crystalline regions when the polymer is cooled. This gives the polymer high rigidity, strength, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Crystalline polymers tend to have high shrinkage and require careful control of processing conditions. Examples of crystalline polymers include PE, PP, PA, and PEEK.
Choosing the right type of plastic extrusion material depends on the desired shape, size, function, and performance of the final product. By understanding the different types of plastic extrusion materials, you can select the best one for your application.
Common Plastic Extrusion Materials
If you are looking for a plastic extrusion material, you might be overwhelmed by the choices. There are many different types of plastics, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. To help you narrow down your options, we have prepared a brief overview of some of the most popular plastic extrusion materials. This is not a complete list, but it will give you an idea of what is out there. Before you make your final choice, you should consider various factors, such as how the material behaves physically, dimensionally, electrically, and thermally.
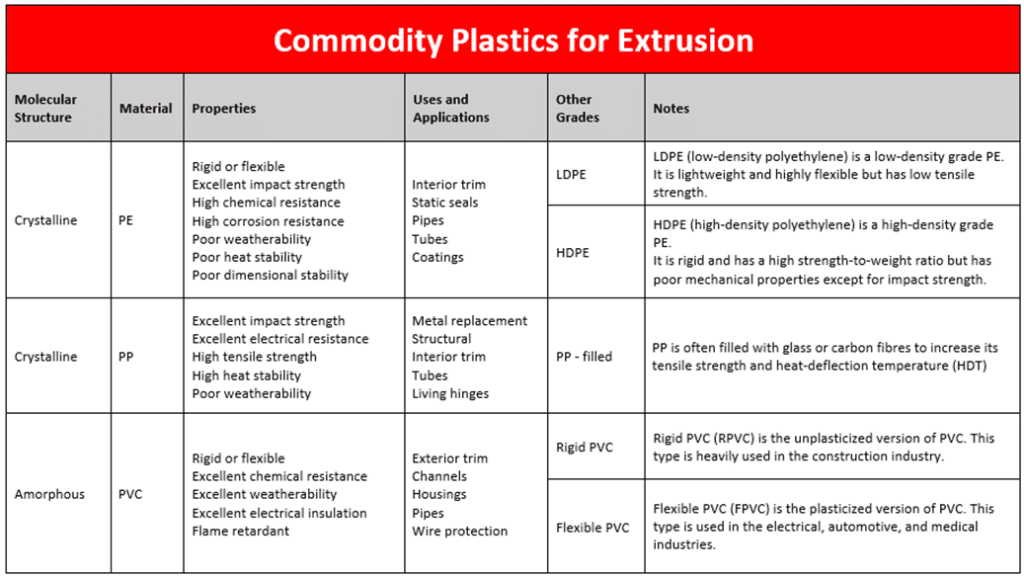
Commodity Grade
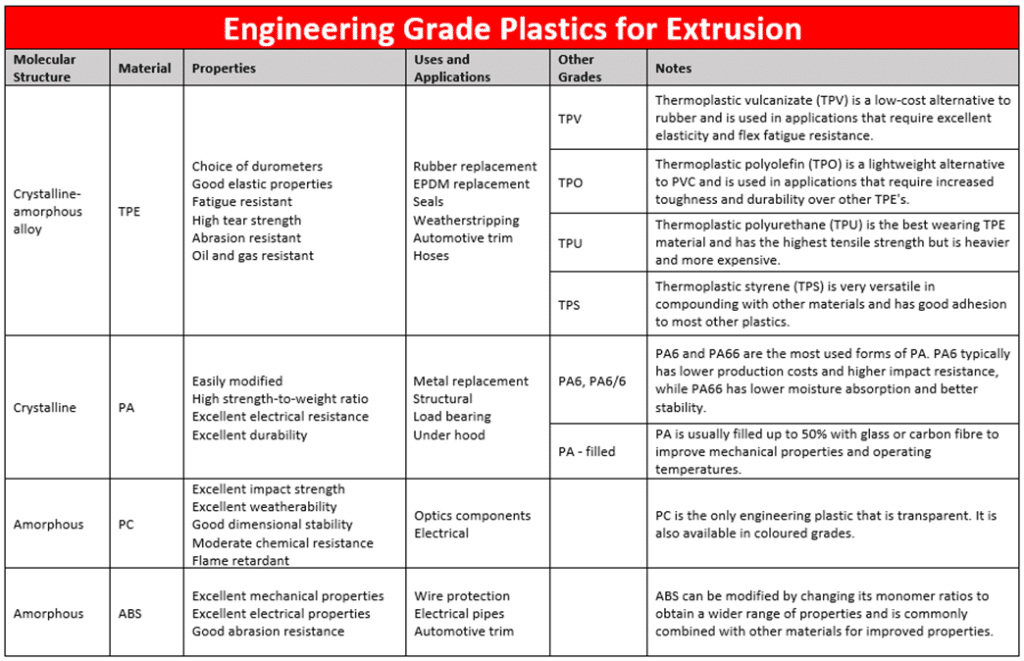
Engineering Grade
What is Reinforcement, Fillers, and Additives in Extrusion?
Reinforcement, fillers, and additives are materials that are added to the plastic resin to enhance its properties or performance in extrusion. They can improve the strength, stiffness, durability, appearance, or functionality of the extruded product.
Reinforcement
Reinforcement is a material that increases the mechanical strength or stiffness of the plastic resin. There are two main types of reinforcement used in extrusion:
- Fiber Reinforcement
Fiber reinforcement is the addition of fibers, such as glass, carbon, or natural fibers, to the plastic resin. The fibers can be short or long, oriented or random, depending on the desired properties and processing method. Fiber reinforcement can improve the tensile strength, modulus, impact resistance, and dimensional stability of the extruded product.
- Coextrusion
Coextrusion is a process that combines two or more different plastic resins in a single extrusion die. The resins can have different colors, properties, or functions, and can form layers or structures within the extruded product. Coextrusion can create complex shapes, enhance aesthetics, or provide functional benefits such as barrier properties, adhesion, or compatibility.
Fillers
Fillers are materials that are added to the plastic resin to reduce its cost, weight, or density, or to modify its properties or appearance. There are two main types of fillers used in extrusion:
- Extender Fillers
Extender fillers are inexpensive materials that are used to increase the volume or bulk of the plastic resin. They can reduce the cost per unit weight of the extruded product, but they may also reduce its mechanical properties or performance. Examples of extender fillers include calcium carbonate, talc, clay, or wood flour.
- Functional Fillers
Functional fillers are materials that are used to improve or modify the properties or performance of the plastic resin. They can enhance the thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, flame retardancy, abrasion resistance, or optical properties of the extruded product. Examples of functional fillers include metal powders, carbon black, graphite, alumina trihydrate, or titanium dioxide.
Additives
Additives are materials that are added to the plastic resin in small amounts to impart specific functions or characteristics to the extruded product. They can improve the processing, stability, durability, appearance, or functionality of the plastic resin. Common additives to plastic extrusion materials include:
- UV inhibitors and stabilizers to prevent UV degradation.
- Adhesion promoters to improve bonding to other materials.
- Internal lubricants to reduce abrasion and prevent sticking.
- Impact modifiers to improve shock and crack resistance.
- Flame retardants to resist combustion.
- Colorants to color and protect against color fade.
- Plasticizers to increase flexibility.
- Foaming and blowing agents to decrease weight.

Selecting a Plastic Extrusion Materials
Selecting a plastic extrusion material is an important decision that depends on several factors, such as:
- The desired shape and size of the extruded product
- The required mechanical and thermal properties of the extruded product
- The environmental conditions and exposure of the extruded product
- The cost and availability of the plastic resin and other materials
- The compatibility and processability of the plastic resin and other materials
The choice of plastic extrusion material should be based on the specific needs and goals of the project. Some of the common properties that should be considered when selecting a plastic extrusion material are:
- Density: The mass per unit volume of the material. It affects the weight and cost of the extruded product.
- Melt temperature: The temperature at which the material becomes fluid and can be extruded. It affects the energy consumption and processing speed of the extrusion.
- Melt viscosity: The resistance of the material to flow when melted. It affects the pressure and shear stress required for extrusion.
- Thermal expansion: The change in volume of the material due to temperature changes. It affects the dimensional stability and shrinkage of the extruded product.
- Tensile strength: The maximum stress that the material can withstand before breaking when stretched. It affects the durability and resistance to deformation of the extruded product.
- Modulus: The measure of stiffness or rigidity of the material. It affects the flexibility and elasticity of the extruded product.
- Impact strength: The ability of the material to absorb energy and resist cracking or breaking when subjected to sudden impact. It affects the toughness and resilience of the extruded product.
- Thermal conductivity: The ability of the material to transfer heat. It affects the heat dissipation and insulation of the extruded product.
- Electrical conductivity: The ability of the material to conduct electricity. It affects the electrical properties and applications of the extruded product.
- Flammability: The tendency of the material to ignite and burn when exposed to heat or flame. It affects the safety and fire resistance of the extruded product.

Get in Touch with Us
Looking for plastic extrusion experts? You’ve come to the right place. We can help you choose the best material and design for your custom extruded product. We have more than 30 years of experience and we offer high-quality products and services at competitive prices. We can work with various plastic materials and extrusion techniques to meet your needs. We can handle any project size, from prototype to production, and we can deliver your products on time and within budget.
We are your trusted partner for manufacturing solutions. Contact us today and tell us about your project.