Die casting is a manufacturing technique that involves injecting molten metal into a mould and forming a desired shape under high pressure. Die casting is suitable for producing parts with complex designs that require accuracy and large-scale production. Some of the common metals used for die casting are zinc, magnesium, and aluminium. However, zinc and aluminium are the most popular choices due to their availability, cost, and properties.
Zinc and aluminium have different characteristics that affect their performance, application, and suitability for die casting. Therefore, it is important to understand the differences between zinc die casting and aluminium die casting and how to choose the right one for your project.
In this blog post, we will compare zinc and aluminium in terms of their properties, advantages, disadvantages, costs, and applications. We will also provide some guidelines on when to choose zinc or aluminium die casting for your project.
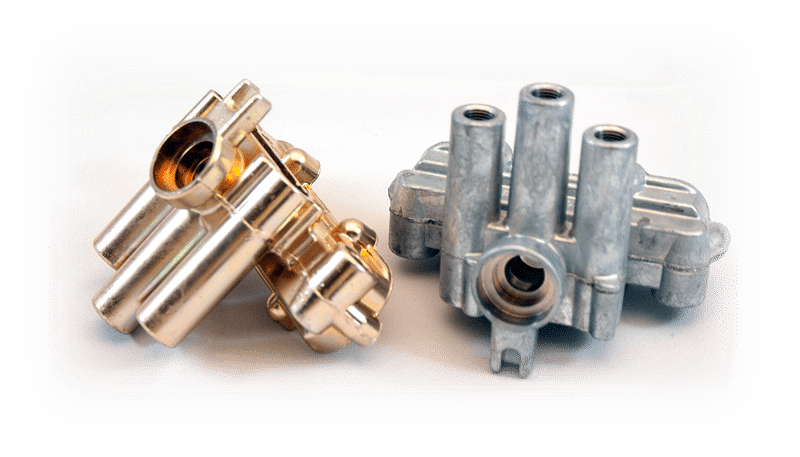
What is Zinc Alloy
Zinc alloy is a metal composed of zinc and other elements such as aluminium, copper, magnesium, or tin. Zinc alloy has a low melting point of about 420°C, which makes it compatible with the hot chamber die casting process. The hot chamber process involves immersing the mould in a molten metal bath and injecting the metal into the mould through a gooseneck and a nozzle. The hot chamber process is faster, cheaper, and more efficient than the cold chamber process.
Zinc alloy has a high density of about 5g/cm3, which makes it heavier and stronger than most die casting materials. Zinc alloy also has excellent thermal conductivity, which means it can absorb and dissipate heat efficiently. Zinc alloy can cast complex, thin-walled, precision parts with smooth surfaces and high dimensional accuracy. Zinc alloy can also accept various surface treatments such as electroplating, spraying, or painting.
What is Aluminium Alloy
Aluminium alloy is a metal composed of aluminium and other elements such as silicon, copper, magnesium, or zinc. Aluminium alloy has a higher melting point of about 660°C, which makes it compatible with the cold chamber die casting process. The cold chamber process involves melting the metal in a separate furnace and transferring it to a shot chamber where it is injected into the mould through a plunger. The cold chamber process is slower, more expensive, and less efficient than the hot chamber process.
Aluminium alloy has a lower density of about 2.7g/cm3, which makes it lighter and more corrosion-resistant than zinc alloy. Aluminium alloy also has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, which means it can conduct electricity and heat well. Aluminium alloy can cast parts with good mechanical properties such as strength, hardness, ductility, and wear resistance. Aluminium alloy can also be machined easily after casting.
Differences Between Zinc vs Aluminium Die Casting
Zinc die casting and aluminium die casting have different properties that determine their advantages and disadvantages in various aspects such as weight, strength, durability, surface quality, cost, etc. Below are some of the main differences between zinc die casting and aluminium die casting:
Weight
Zinc die castings are heavier than aluminium die castings due to their higher density. This can be an advantage or a disadvantage depending on the application. For example, heavier parts can provide more stability and impact resistance for structural applications, while lighter parts can reduce fuel consumption and increase performance for automotive applications.
Strength
Zinc die castings are stronger than aluminium die castings due to their higher density and lower porosity. Zinc die castings can withstand higher loads and pressures without deforming or breaking. However, zinc die castings are more prone to aging than aluminium die castings due to their lower thermal stability. Aging can cause zinc die castings to expand in volume, reduce in strength, and deform or crack over time.
Durability
Aluminium die castings are more durable than zinc die castings due to their lower density and higher corrosion resistance. Aluminium die castings can resist oxidation and rust better than zinc die castings in humid or salty environments. However,
aluminium die castings are more susceptible to fatigue than zinc die castings due to their lower hardness and higher ductility. Fatigue can cause aluminium die castings to crack or fail under repeated stress cycles.
Surface Quality
Zinc die castings have better surface quality than aluminium die castings due to their lower melting point and higher fluidity. Zinc die castings can fill the mould more easily and produce smoother surfaces with finer details and tighter tolerances. Zinc die castings can also be polished and electroplated more easily than aluminium die castings due to their lower porosity and higher compatibility with various coatings. However, zinc die castings are more sensitive to temperature changes than aluminium die castings and can warp or shrink during cooling or heating.
Cost Zinc die castings are cheaper than aluminium die castings due to their lower melting point and higher compatibility with the hot chamber process. Zinc die castings can reduce the energy consumption, cycle time, and mould wear of the die casting process, resulting in lower production costs. However, zinc die castings are more expensive than aluminium die castings in terms of material costs due to their higher density and similar price per unit weight.

When to Choose Zinc Die Casting for your Project
Zinc die casting is a good choice for your project if you need parts that have:
Thin Walls
With zinc die casting you can create parts with thin walls (as low as 0.3mm) using zinc, thanks to its high fluidity and low injection pressure. This means you can save on weight and material cost without compromising on strength and rigidity.
Harsh Environmental Conditions
Zinc die casting can make parts that can endure harsh environmental conditions, such as humidity, salt spray, or chemicals, using zinc, thanks to its high corrosion resistance and durability. Zinc also has high hardness and impact resistance, which means your parts can resist wear and tear better than other metals.
Lesser Residual Stress
Zinc is a great material for making parts with intricate shapes and fine details. It flows easily and needs less pressure to inject into the mould. It also has a lower melting point and less chance of damaging or corroding the mould. This means you can save money and time on your die cast mould maintenance and replacement.
Faster Production
One of the advantages of using zinc for die casting is its faster production speed. Zinc has a lower melting point and a higher solidification rate than aluminium, which means it can fill the mould more quickly and efficiently. Zinc also works well with the hot chamber process, which reduces the cycle time and production cost of die casting.
When to Choose Aluminium Die Casting for your Project
Aluminium die casting is a good choice for your project if you need parts that have the following characteristics:
Strength-to-weight ratio
Aluminium die casting can produce parts with high strength-to-weight ratio due to its low density and high tensile strength. Aluminium die casting can also reduce the weight and material cost of the parts while maintaining their performance and functionality.
High Operating Temperatures
Aluminium die casting can produce parts that can withstand high operating temperatures (up to 300°C) due to its high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion. Aluminium die casting can also prevent thermal fatigue and deformation of the parts due to its high heat resistance and stability.
Electrical Conductivity
Aluminium can produce parts that have high electrical conductivity due to its high percentage of aluminium. Aluminium die casting can also improve the electrical efficiency and functionality of the parts due to its low electrical resistance and energy loss.

Conclusion
Zinc and aluminium die casting are both versatile and cost-effective methods of producing high-quality metal parts with complex designs and fine details. However, they have different properties, differences, and applications that you need to consider before choosing one for your project. Zinc is more suitable for parts that require thin walls, harsh environmental conditions, lesser residual stress, die cast mould, or faster production. Aluminium is more suitable for parts that require strength-to-weight ratio, high operating temperatures, electrical conductivity, or anodizing or painting. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each metal, you can make an informed decision that meets your project requirements and expectations.



